January 27, 2025 from Medscape
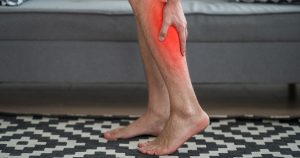
When a healthy 74-year-old woman presented with frequent nocturnal calf cramps—occurring four to five times per week—the recommended treatment wasn’t a supplement or a medication. Instead, she was advised to begin regular calf-stretching exercises, the most evidence-supported strategy for preventing these painful, sleep-disrupting episodes.
Nocturnal leg cramps are a frequent complaint among older adults, affecting an estimated 40% of individuals over age 50. These cramps, which commonly strike during sleep, can reduce overall sleep quality and lead to fatigue and diminished quality of life.
Dr. Douglas Paauw, professor of medicine at the University of Washington, commented that
“The best option for muscle cramp prevention is stretching exercises.”
Stretching Shows Strong Evidence
Multiple studies have shown that stretching—particularly of the calf and hamstring muscles—is a reliable and safe intervention. One study by Hallegraeff et al. found that patients over age 55 who performed nightly calf and hamstring stretches had significantly fewer and less severe cramps than those who did not.
Another randomized trial by Tapper and colleagues compared stretching to meditation in patients experiencing more than four nocturnal cramps per week. Both groups saw reduced severity, but stretching remains the preferred approach due to its simplicity and physical benefit.
What Else Works—And What Doesn’t
Although magnesium is commonly used as a supplement for muscle cramp relief, the evidence doesn’t support its effectiveness. A Cochrane review found that magnesium was unlikely to provide meaningful benefit for older adults experiencing skeletal muscle cramps.
Some medications have been investigated, but most come with drawbacks. Quinine was previously popular but has since been restricted due to safety concerns. Hydroxychloroquine, spironolactone, and verapamil have been explored but are not standard recommendations for this condition.
Dr. Paauw also cautions clinicians to review medications before diagnosing idiopathic cramps, noting that beta-agonists and potassium-sparing diuretics, including spironolactone, can trigger cramps.
Promising New Therapies
Recent studies suggest new directions for research and treatment. In a randomized controlled trial, vitamin K2 supplementation significantly reduced the mean weekly frequency of cramps from over three per week to fewer than one. This result was statistically significant and well-tolerated.
Another small trial looked at patients with cirrhosis experiencing frequent leg cramps. When treated with taurine supplements, patients reported a statistically significant reduction in cramp frequency, duration, and severity.
“Vitamin K2 supplementation looks like a promising and safe option,”
said Dr. Paauw.
Key Takeaway
For older adults experiencing frequent nocturnal leg cramps, calf-stretching exercises should be the first-line intervention. While supplements like vitamin K2 may offer added benefit in the future, stretching remains the most evidence-based and accessible method to reduce cramp frequency and severity.
Patients should also be assessed for underlying causes or contributing medications, and where appropriate, non-pharmacologic strategies should be emphasized. With consistent stretching and informed care, the burden of nocturnal leg cramps can be effectively reduced.
Considering an IME or document review to resolve an insurance claim, legal file, or workplace health and safety issue?
Our specialists provide evidence-based opinions, so get in touch with Western Medical today to learn more about our services.

